Editorial
-
International Conference on Building Envelope Systems and Technologies – ICBEST is the premier conference for attendees to benefit from the cutting edge information on building envelope systems and technologies. ICBEST is a worldwide forum for building envelope architecture and engineering. It provides information exchange, networking, and discussions of recent developments and their application thus bridging the gap between architects, designers, engineers, manufacturers, and researchers
Articles
-
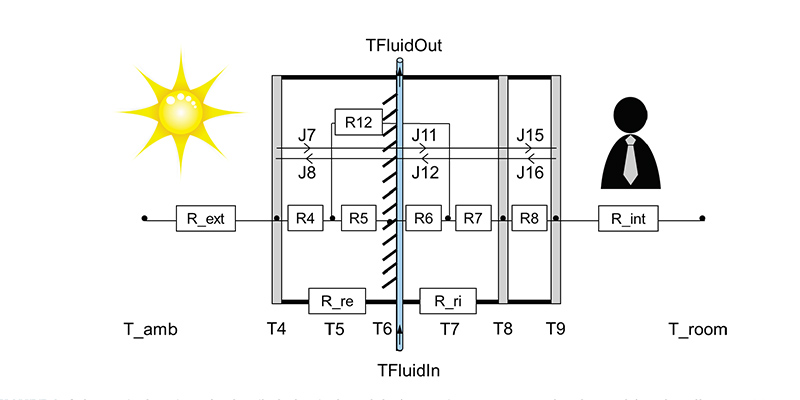
The paper presents an innovative approach to the retrofitting of the adaptive ventilated facade module developed in the EU project E2VENT. The E2VENT innovative facade module is targeted to Optimal Adaptability and Heat Exchange for the refurbishment of existing buildings and is composed of two main parts: an adaptable smart modular heat recovery unit (SMHRU), which is adjustable to work within the ventilated façade cavity, is able to recover heat from ventilation air, and can preheat ventilation air in winter while precooling it in summer; and a latent thermal heat energy...
-
These days, we are constantly expecting more from the performance of the building envelope with regard to both comfort and ecological compatibility. Operational energy has been undergoing significant improvement, which in turn draws attention to the building matter: If a standard building does not consume energy in its operation, then it is the building material that impacts the level of environmental compatibility. Designing with used building matter offers an opportunity to decrease emissions from extraction, preserve primary resources and reduce landfill. On top of that,...
-
The development of adaptive building envelopes is receiving increasing interest in contemporary architecture, as it strives to cope with several requirements such as energy saving and harvesting (or mitigating environmental actions), improving performance and, finally, aesthetics. Actual implementation fundamentally concerns external “skins” (i.e. adaptive façades), but internal “skins” (e.g. adaptive ceilings) may also be developed.
The engineering aspects related to the above developments are quite complex and involve different behavioral models to be merged...
-
The new calculation tool EvalDRC enhances current strategies for the simulation of Daylight Redirecting Components (DRCs). It is built upon RADIANCE as a core simulation engine and uses the daylight coefficient method, climate based sky models for annual simulations, and daylight metrics for data reduction. Contribution Photon Mapping is introduced as a new method for physically correct DRC simulation. Further new features are separate: True Sun Coefficients for a less approximated, more accurate treatment of the sun contribution and monthly breakdowns of the Spatial...
-
Active building envelopes have provided cost reductions of 40% compared to the separate installation of solar collectors on a building envelope. However, solar building envelopes are more complex than conventional building envelopes due to their additional solar function. Firstly, the paper explains this complexity before describing methods of handling it. The focus of the simulation models is to obtain high levels of accuracy at low costs. From the development of innovative solar envelopes to the general planning and construction of solar architecture, this paper provides...
-
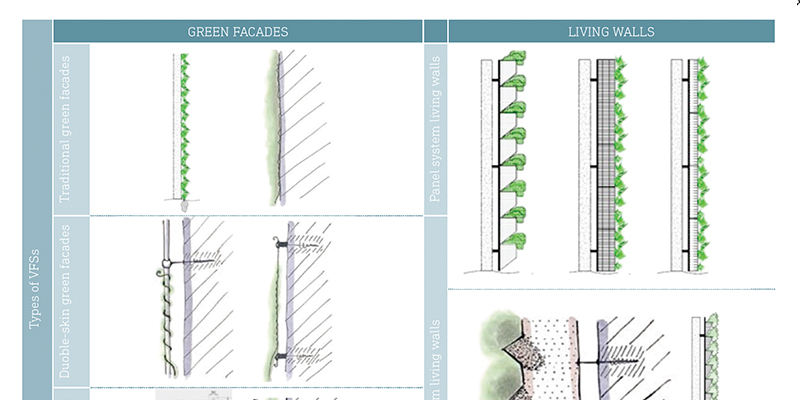
The decline of green spaces through urbanization, the urban heat island effect resulting from the use of materials with low albedo value, and the greenhouse effect occurring as a result of the consumption of fossil fuels all lead to an increase in ambient air temperature. Use of roof, facade, and pavement materials with high albedo value and vegetated surfaces play an important role in reducing the urban heat island effect. It is essential to use renewable energy sources instead of fossil fuels and/or reduce energy consumption in order to decrease the greenhouse effect. There are various...
-
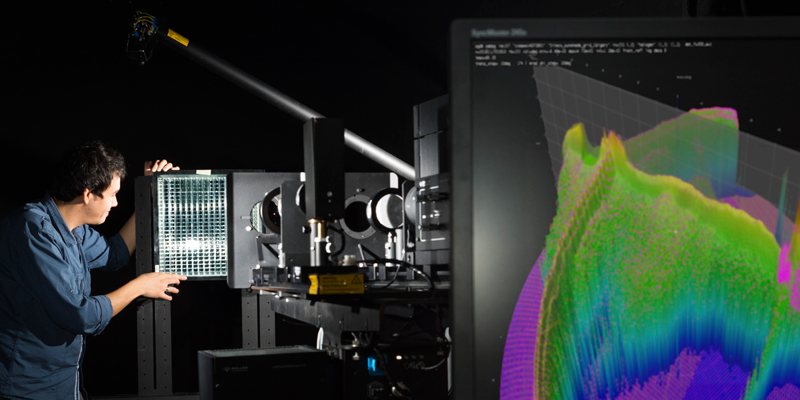
Daylight Redirecting Components (DRCs) guide daylight to zones with insufficient daylight exposure. They reduce energy demand for lighting, heating and cooling, and improve visual and thermal comfort. The data-driven model in Radiance is a means to model DRCs in daylight simulation. Rather than internal optical mechanisms, their resulting Bidirectional Scattering Distribution Function (BSDF) is replicated.
We present models of two DRCs that are generated from measurements. The impact of the following three necessary steps in the generation of data-driven...
-
Building façades are Engineer-To-Order (ETO) products and, as such, they show unique features on a project-by-project basis. The partitioning of design tasks during the design and manufacturing process of these products, however, does not fully capture how specific design decisions influence other stakeholders’ choices. This lack of design integration is most severe at early stages when a large proportion of initial costs, mostly driven by manufacturability aspects, is determined. This paper illustrates a methodology to build Knowledge-Based Engineering (KBE) applications to...
Applied practice
-
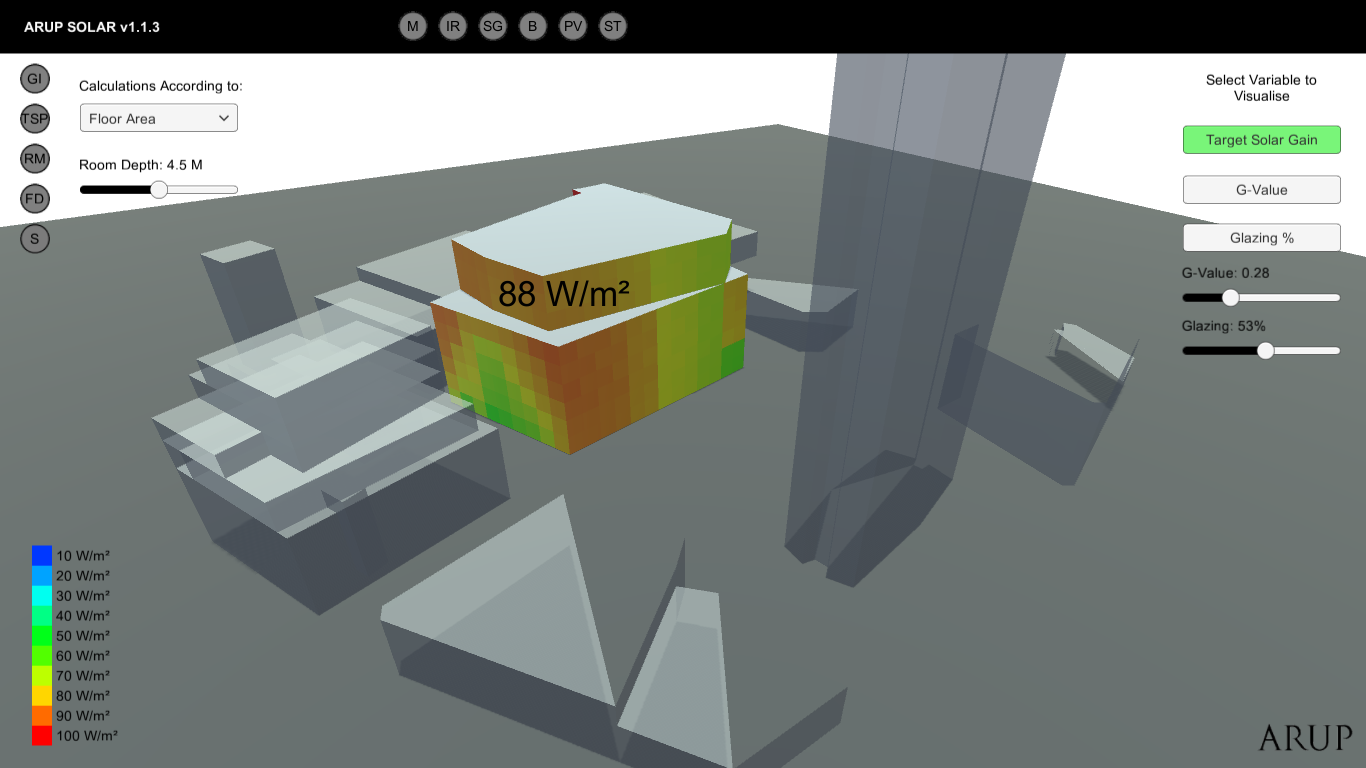
During early project stages, design teams need to explore a wide range of possible envelope configurations in order to identify those that best address the project constraints and objectives.
Crucial aspects such as control of solar gains, use of blinds and renewable energy production are typically the subjects of extensive discussions among architects and façade, mechanical, electrical and PH engineers. Traditional methodologies used to inform the design on such matters are neither flexible nor time efficient, failing to meet the expectations of the team....