Guest Editors: Jan Belis and Christian Louter
Glass as a building material demonstrates the nature of the architectural discipline, where science and building practice are closely linked. Papers show new research findings as well as new practical application.
Editorial
-
Facade Design and Engineering is a multidisciplinary field that touches many other scientific disciplines. Glass is one of the key materials for building envelopes, and a strong scientific community has developed over the last decade. Designers love glass for its transparency. It is strong but brittle and very demanding in terms of engineering. We continuously see new innovative developments in terms of its climatic performance, structural possibilities, construction design and new applications. Reason enough to dedicate this special issue to the topic. The issue would not have been...
Articles
-
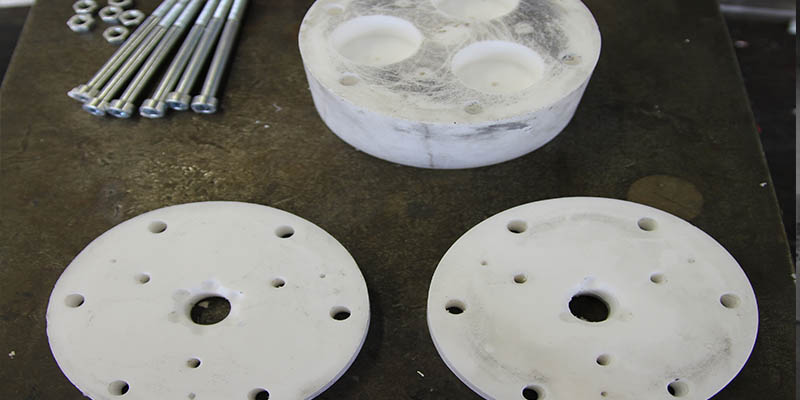
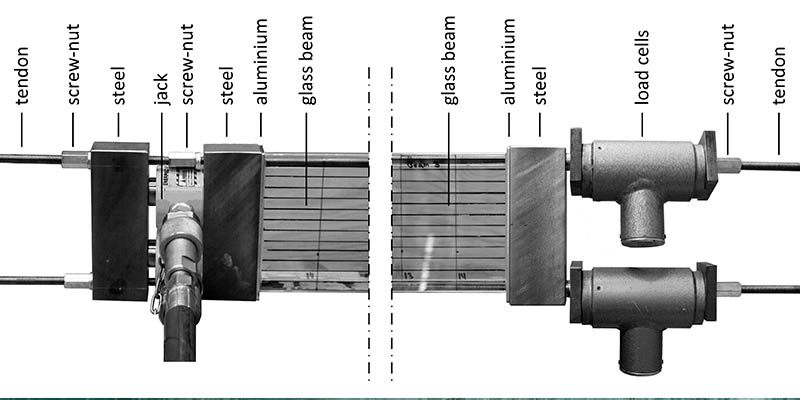
The mechanical response of post-tensioned glass beams is explored in this paper. This is done through bending experiments on post-tensioned glass beam specimens with either mechanically anchored or adhesively bonded steel tendons by which a beneficial pre-stress is inflicted on the glass beams. In addition, reference beams with identical geometry but without tendons are tested. From the results of the bending experiments it can be seen that the post-tensioned glass beams reach higher initial fracture loads than the reference glass beams. Furthermore, the post-tensioned glass beams...
-
Permasteelisa Group developed with Fiberline Composites a new curtain wall system (Thin Environmental Cladding or TEC), making use of pultruded GFRP (Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer) material instead of traditional aluminum. Main advantages using GFRP instead of aluminum are the increased thermal performance and the limited environmental impact. Selling point of the selected GFRP resin is the light transmission, which results in pultruded profiles that allow the visible light to pass through them, creating great aesthetical effects. However, GFRP components present also weaknesses, such...
-
The highest transparency in glass facades is obtained with point fitted glass units. Point fitted insulating glass units minimize thermal bridging and lead to glass facades with better energy efficiency. Though, insufficient knowledge is present to offer a design method for point fittings in insulating glass. Therefore research has been carried out to extend the existing SLG-design-method (Linear superposition of local and global stress components) of Beyer for point fitted single and laminated glass to insulation glass units. This paper presents the first results of this research...
-
In the last years an increase of the number of building projects with built-in curved glass can be observed. The applications can principally be curved monolithic glass, laminated safety glass or insulated glass. This fact makes it absolute of interest to make more investigations in this field. The investigations can be focused on e.g. the process of the bending of the glass to bring it into a certain shape, or the very difficult topic of pre-stressing it. The state of the art of the production process of such glass shows some different ways to produce curved glass. The most used way is...
-
The recent demand for architectural transparency has drastically increased the use of glass material for structural purpose. However, connections between structural glass members represent one of the most critical aspects of glass engineering, due to the fragile behaviour of this material. In that respect, research activities on adhesive point-fixings are currently on-going. The mechanical behaviour of adhesive point-fixings is affected by large nonlinearities, which are usually investigated by nonlinear Finite Element Analysis (FEA). This paper focuses on the geometrical and the...
-
A reinforced glass folded structure has been developed using an innovative connection method. The concept relies on extending the reinforcement outwards from the laminated glass and using it to transfer a significant part of the load. The goal is to accomplish a glass element with high stiffness, connected by using a discrete almost invisible and easily assembled/disassembled mechanism. This paper addresses the main issues regarding the design and fabrication of a 90° folded structure, the experimental investigation of the out-of-plane compressive response and the construction of a...