Editorial
-
The PowerSkin conference series is a biennial event organised cooperatively between TU München, TU Darmstadt, and TU Delft, which is already in its third edition, having started in 2017. The conference aims to address the role of building skins in accomplishing a carbon neutral building stock. The presented papers showcase recent scientific research and developments as well as projects related to building skins from the perspectives of material, technology, and design.
Topics such as building operation, embodied energy, energy generation and storage in context of the envelope,...
Articles
-
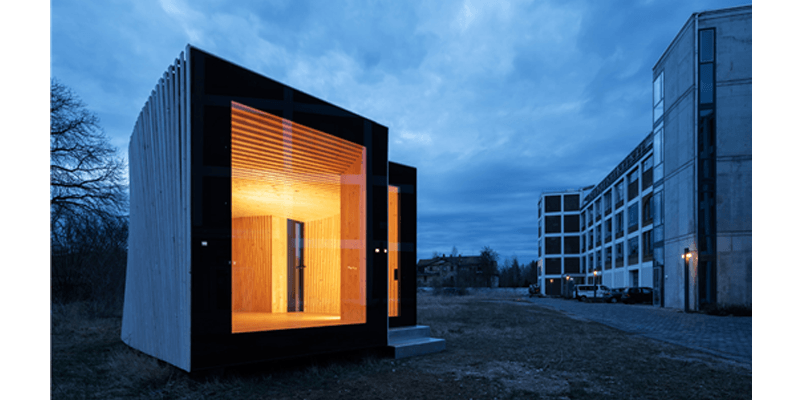
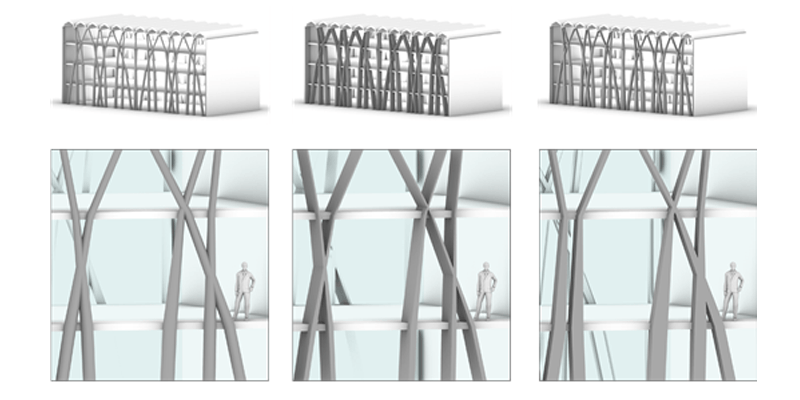
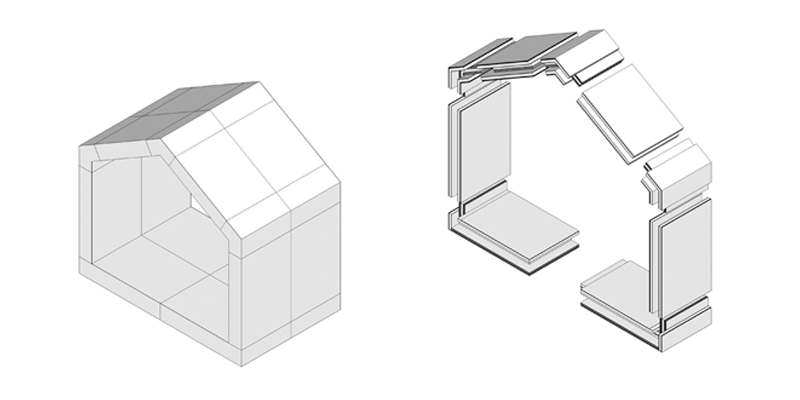
The project seeks to create a building envelope that functions as structure, enclosure, and insulation, which is assembled from one solid timber construction element type. Wood has clear environmental benefits when compared to other standard construction materials such as steel and concrete, a good strength-to-weight ratio, relatively high thermal insulation, and low production costs. This research seeks to leverage these characteristics to simultaneously reduce the number of material layers in timber building envelopes while improving the building physics performance. Thus, the...
-
The potential of exemplary organic and inorganic Phase Change Materials (PCMs) as façade integrated storage is tested. The impact of two PCMs on heat flows is assessed in comparison with water and concrete. The simulation-study employs a transient Modelica simulation model of a test cell featuring the Solar Energy Balanced Façade (SEBF). It is shown that, when compared to water, PCMs of identical volume change the seasonal energy balance in winter and summer by only ± 4%. Other than water, the PCMs maintain this effect even if the storage volume decreases. Due to spatial constraints,...
-
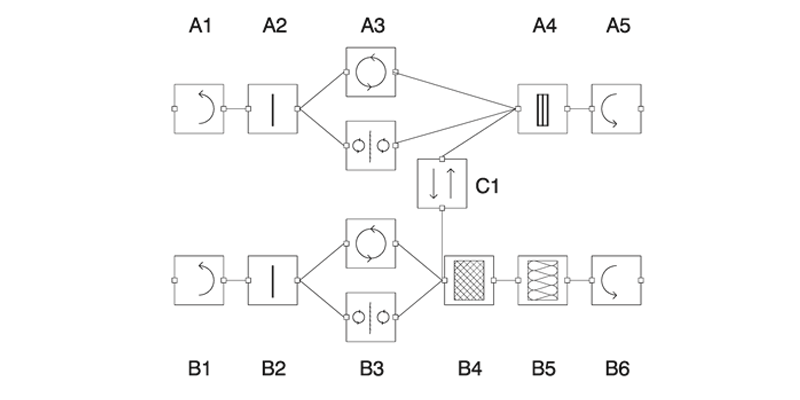
The design of building envelopes requires a negotiation between qualitative and quantitative aspects belonging to different disciplines, such as architecture, structural design, and building physics. In contrast to hierarchical linear approaches in which various design aspects are considered and conceived sequentially, holistic frameworks allow such aspects to be taken into consideration simultaneously. However, these multi-disciplinary approaches often lead to the formulation of complex high-dimensional design spaces of solutions that are generally not easy to handle manually....
-
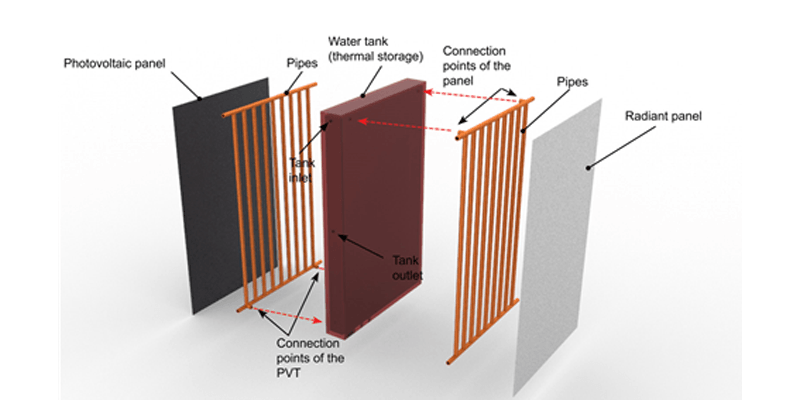
Hybrid photovoltaic/thermal (PVT) systems combine electric and thermal energy generation and provide noiseless operation and space-saving features. As the efficiency of photovoltaic (PV) panels increases at low surface temperatures, this paper suggests combining the PVT panel with a radiant cooling and heating panel in one system. A thermal storage tank fluidly connects the heat-exchanging pipes at the back of the PVT system and radiant panel. The upper portion of the tank feeds the radiant panel and the lower portion of the tank is connected to the PVT system. The proposed device is...
-
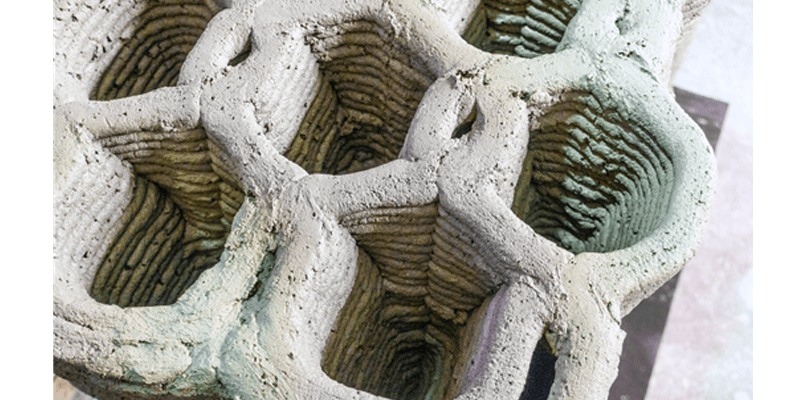
Building envelopes incorporate a multitude of functions, such as structure, room enclosure, insulation, and aesthetic appeal, typically resulting in multi-material layered constructions. With the technology of additive manufacturing, geometrical freedom can instead be utilised to integrate functional requirements into mono-material building components. In this research, the additive manufacturing method of lightweight concrete extrusion and its potential for thermal performance via geometric customisation is explored. It investigates whether the insulating performance of wall components...
-
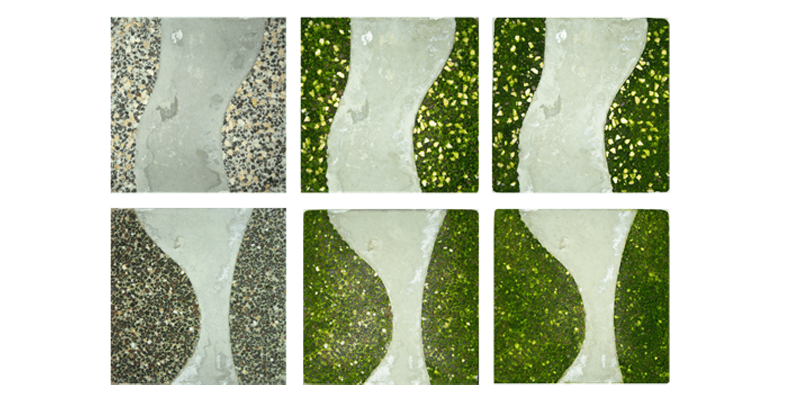
A bioreceptive material allows for biological content (biofilms) to grow on it, without necessarily affecting the material itself. If a bioreceptive concrete could therefore be integrated into a building façade, it could lead to green façades that do not need additional technical systems. As part of previous research by the authors, a promising bioreceptive concrete mixture was formulated. The aim of this research is to develop this concept by using the previously developed mixture to create a bioreceptive concrete façade panel prototype, made using commonly available materials, that can...
-
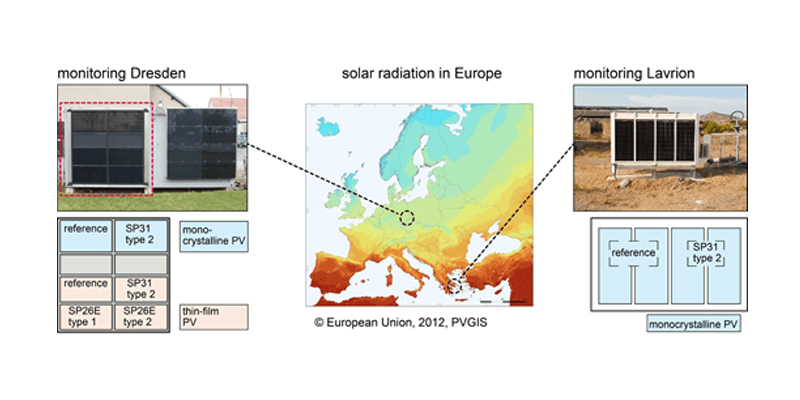
Since façade-integrated photovoltaic (PV) modules heat up greatly, which reduces the efficiency of the PV, façade panels with PV and phase change materials (PCM) were developed. PCMs absorb a significant amount of thermal energy during the phase transition from solid to liquid, while maintaining a specific melting temperature. This cools down the PV and increases the electrical yield. Numerical studies on PV-PCM warm façades without rear-ventilation have so far been missing. Therefore, a thermal and an electrical simulation model for PV-PCM warm façades were developed and validated. They...
-
The research project ADAPTEX pursues the goal of developing adaptive, energy-efficient textile sun shading systems using the smart material Shape Memory Alloy (SMA). Within this approach lies a high potential for novel sun protection systems demanding little energy or even self-sufficiently adapting to external stimuli while reducing operation and maintenance costs and at the same time offering solutions to tackle growing demand for sun and glare protection. A Design Categories Matrix is presented that brings together various involved fields from textile design and façade construction to...
-
According to the UNHCR, in 2019 there were 70.8 million refugees worldwide. Due to war, catastrophes, and emergency situations a great demand for temporary accommodation has arisen within the last couple of years. The main requirements for these shelters are protection for the inhabitants, easy transportability, and quick construction. In addition, in terms of resource efficiency, the recyclability of the construction materials is of great importance. Paper materials have a high potential for this, due to their strong structure, cost-effective production, and optimised recycling...
-
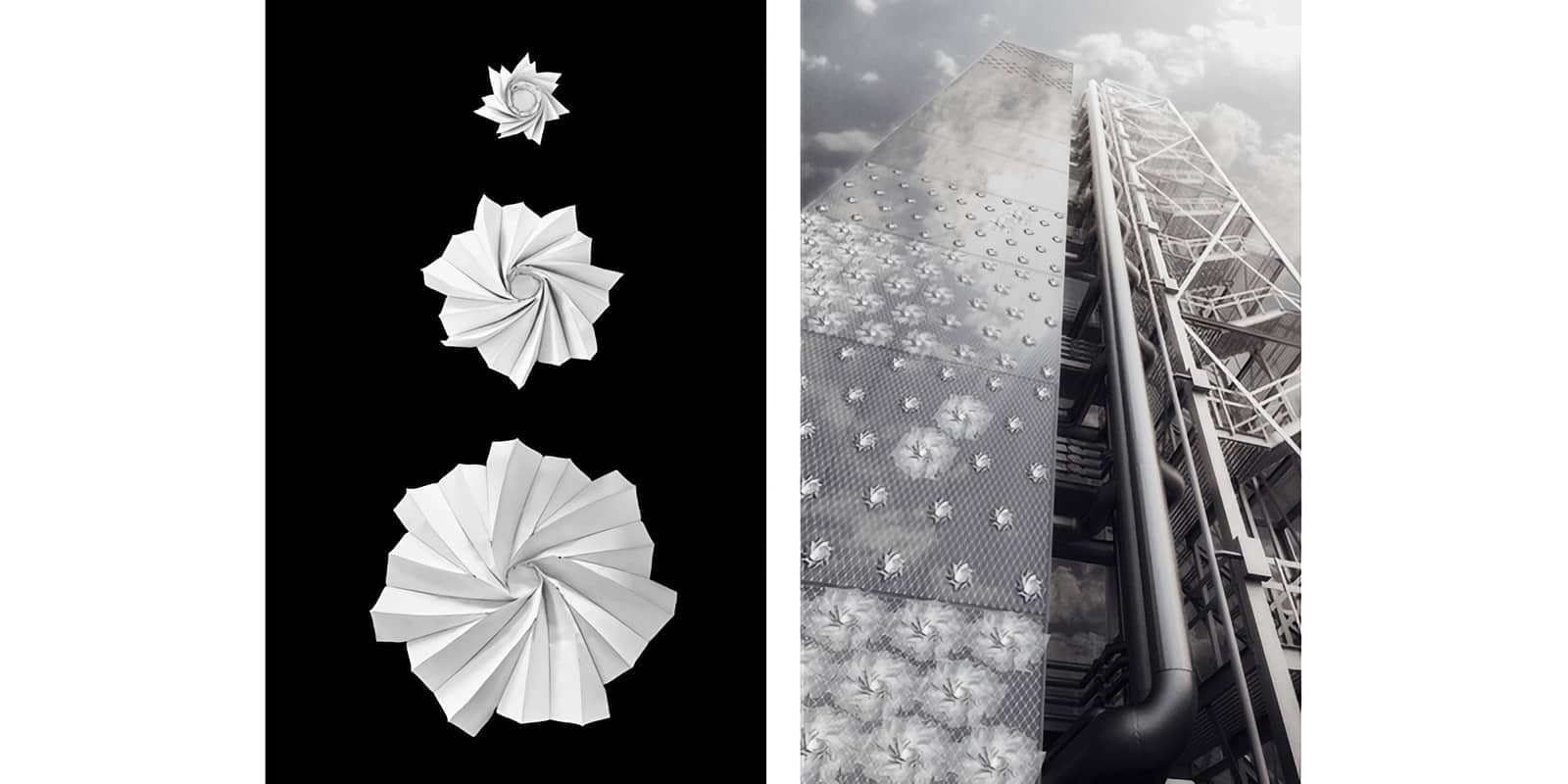
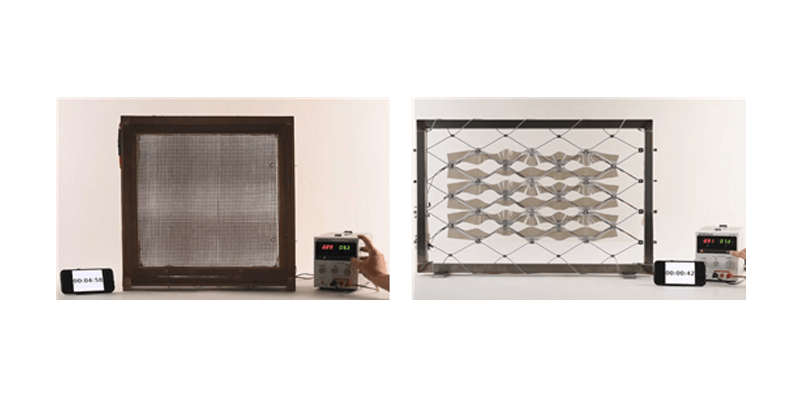
This paper describes the development of an innovative, material- and energy-efficient façade concept: a pneumatically actuated Origami sun shading system - abbreviated “PAOSS” - which combines the aesthetic and material-immanent qualities of textile materials with the functional aspects of a controlled and targeted light transmission regulation by means of integrated active pneumatic components (Fig. 1).
Due to the possibility of reducing a given surface to a minimal form, textile-based folding structures are highly suitable for selective sun and glare protection systems, in order...